Code
# install.packages("randomForest")
# install.packages("caret")
library(randomForest)
library(caret)July 11, 2024
Random Forest is a powerful ensemble learning method used for classification and regression tasks. It operates by constructing multiple decision trees during training and outputting the mode of the classes (classification) or mean prediction (regression) of the individual trees. This method improves the model’s accuracy and reduces overfitting. R provides excellent packages such as randomForest and caret to build and evaluate random forests.
Data Preparation: Cleaning and preparing data for analysis.
Model Training: Building the random forest model.
Model Evaluation: Assessing the model’s performance.
Prediction: Using the trained model to make predictions on new data.
Let’s walk through an example using a random forest model to classify species in the iris dataset.
r
# install.packages("randomForest")
# install.packages("caret")
library(randomForest)
library(caret)# Load the data
data <- iris
# Split the data into training and testing sets
set.seed(123)
train_index <- createDataPartition(data$Species, p = 0.8, list = FALSE)
train_data <- data[train_index, ]
test_data <- data[-train_index, ]Random Forest
120 samples
4 predictor
3 classes: 'setosa', 'versicolor', 'virginica'
No pre-processing
Resampling: Bootstrapped (25 reps)
Summary of sample sizes: 120, 120, 120, 120, 120, 120, ...
Resampling results across tuning parameters:
mtry Accuracy Kappa
2 0.9475159 0.9203020
3 0.9455403 0.9172896
4 0.9471579 0.9197251
Accuracy was used to select the optimal model using the largest value.
The final value used for the model was mtry = 2.Assess the model’s performance on the testing set.
# Make predictions on the testing set
predictions <- predict(model, newdata = test_data)
# Create a confusion matrix
conf_matrix <- confusionMatrix(predictions, test_data$Species)
print(conf_matrix)Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction setosa versicolor virginica
setosa 10 0 0
versicolor 0 10 2
virginica 0 0 8
Overall Statistics
Accuracy : 0.9333
95% CI : (0.7793, 0.9918)
No Information Rate : 0.3333
P-Value [Acc > NIR] : 8.747e-12
Kappa : 0.9
Mcnemar's Test P-Value : NA
Statistics by Class:
Class: setosa Class: versicolor Class: virginica
Sensitivity 1.0000 1.0000 0.8000
Specificity 1.0000 0.9000 1.0000
Pos Pred Value 1.0000 0.8333 1.0000
Neg Pred Value 1.0000 1.0000 0.9091
Prevalence 0.3333 0.3333 0.3333
Detection Rate 0.3333 0.3333 0.2667
Detection Prevalence 0.3333 0.4000 0.2667
Balanced Accuracy 1.0000 0.9500 0.9000Examine the importance of each feature in the model.
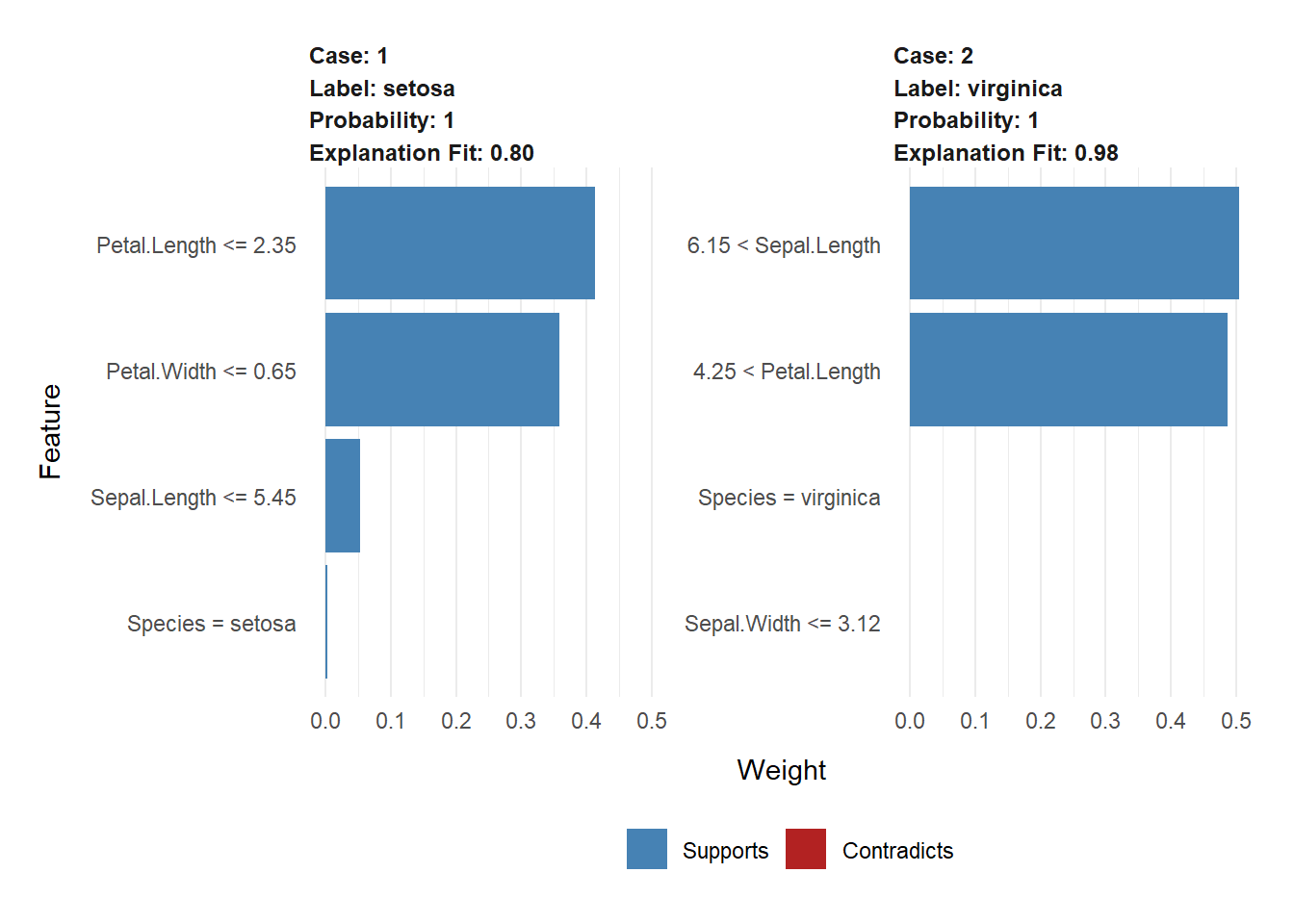
Use the trained model to make predictions on new data.
[1] setosa virginica
Levels: setosa versicolor virginicanew_data$Species <- new_predictions
new_data Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
2 6.5 3.0 5.2 2.0 virginicalibrary(lime)
e <- lime(new_data, model, n_bins = 4)
explanation <- explain( x = new_data,
explainer = e,n_labels = 1,
n_features = 4)
plot_features(explanation)